Какво е Електромотор?
И на електрически мотор е машина, която преобразува електрическа енергия в механична енергия чрез електромагнитни взаимодействия. Основният принцип на функциониране включва взаимодействието между магнитно поле и проводници с ток за генериране на движение. Електродвигателите се използват широко в различни приложения като вентилатори, насоси, компресори и хидравлични системи, поради техния надежденост, ефективност и разнообразие на мощности.

Видове електродвигатели
Има няколко вида електродвигатели, всеки от които е предназначен за различни приложения:
АС Двигатели (Алтернативен Ток):
- Индукционни двигатели (Несинхронни) : Често срещани в индустриални приложения. Ниска цена, надеждни и прости.
- Синхронни двигатели : Поддържат постоянна скорост независимо от натоварването. Подходящи за прецизни приложения.
ДС Двигатели (Постоянен Ток):
- Двигатели с щетки : Прости и евтини, но изискват поддръжка за щетките.
- Двигатели без щетки : Повече ефективни и траещи, но по-скъпи.
Сервомотори : Осигуряват прецизен контрол върху ъгловата позиция, скоростта и ускорението. Често се използват в роботика и CNC машини.
Коракови двигатели : Се движат в дискретни стъпки и са подходящи за приложения, които изискват прецизно позициониране.

Как да изберете правилния електродвигател за хидравлична система
При избора на правилния електродвигател за хидравлична система трябва да се вземат предвид следните ключови фактори:
1. Мощностни изисквания (Конски сили или кВ)
- Мощностното изискване на хидравличния насос е критичен фактор. Двигателите трябва да предоставят достатъчна мощност, за да привеждат хидравличния насос ефективно, без да се прекаредят.
- Изчислете мощността на мотора по формулата:
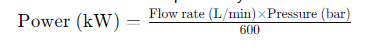
2. Скорост (rpm)
- Електрическите мотори трябва да отговарят на необходимата скорост на хидравличния насос, обикновено указана в обороти в минута (RPM).
- Много хидравлични насоси работят в диапазона от 1200 до 1800 RPM. Скоростта на мотора трябва да е съвместима с този диапазон.
3. Момент
- Хидравличните системи могат да генерират високи моментни натоварвания, особено при стартиране под налягане. Моторът трябва да осигурява достатъчен стартов момент.
- Моментът на мотор може да бъде изчислен от натискът и потока, които системата изисква.
4. Напрежение и електропитащо устройство
- Моторите са налични в различни конфигурации на напрежение, като еднофазови (120V, 240V) или трифазови (208V, 480V и т.н.).
- Изберете мотор, който отговаря на наличното електрическо питащо устройство в вашето предприятие.
5. Дюти цикл
- Задумайте се колко дълго моторът ще работи непрекъснато. Някои мотори са проектирани за прерывисто функциониране, докато други могат да работят непрекъснато без да се прегреят.
- Хидраулическите системи често изискват мотори с висок рабоч цикъл, за да гарантират непрекъснатото функциониране без прегрев.
6. Околна среда
- Има значение да се вземат под внимание околните условия, като температура, влажност и експозиция към прах или химикали.
- Моторите, проектирани с IP класификации (защита от проникване), могат да бъдат избрани, за да се осигури подходяща защита при тежки условия.
7. Ефективност
- Мотори с висока ефективност (например, мотори от клас IE3 или IE4) спестяват енергия и намалят операционните разходи, особено при големи мащаби или непрекъснато функциониране.
- За хидраулически системи, които работят продължително време, енергоефективните мотори могат да направят голяма разлика в операционните разходи.
8. Управление на мотора и метод за стартиране
-
Моторите, използвани в хидраулическите системи, често изискват прецизно управление, по-специално по време на стартирането. Вариантите включват:
- Стартери с пряко свързване (DOL) за малки мотори.
- Меки стартери за ограничаване на пусковия ток и механическото напрежение в мотора.
- Променящи честота приводи (VFDs) за динамичен контрол на скоростта и моментът на мотора.
9. Моторен каркас и монтиране
- Размерът на каркаса и типа монтиране трябва да отговарят на физическите ограничения на устройството на хидравличната система.
- Проследете да е сигурно, че моторът е съвместим с конфигурацията за монтиране на насоса.
10. Цена и наличност
- При избора на мотор, цената трябва да отговаря на вашия бюджет, а наличността на мотора трябва да отговаря на времето на вашия проект. линии.
Заключение
Изборът на правилния електромотор за хидравлична система включва съответствие между мощността, скоростта и момента на хидравличния насос с мотора. Проследете да бъде убедено, че моторът е проектиран за средата и условията на употреба, които ще срещне, и че отговаря на спецификациите за монтиране и електрическо осигуряване на системата.
HCIC е професионален производител на хидравлични системи, основно засягащ се на проектиране, производство, инсталиране, преобразуване, пускане на хидравлични системи и продажба на марки хидравлични компоненти, както и технически услуги. Надяваме се продуктът ни да помогне за намаляване на вашите разходи и подобряване на качеството. За повече информация ни пишете на "[email protected]" или G търсете в Google "HCIC hydraulic"

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 CA
CA
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 KA
KA












