What is a Hydraulic Reservoir?
Sep 06, 2024
A hydraulic reservoir (also called a hydraulic tank) is a container used to store hydraulic fluid in a hydraulic system. It serves multiple functions beyond simply holding fluid. Hydraulic systems use incompressible fluid to transmit power, and the reservoir plays a crucial role in maintaining the proper operation of the system by supplying, conditioning, and cooling the fluid.
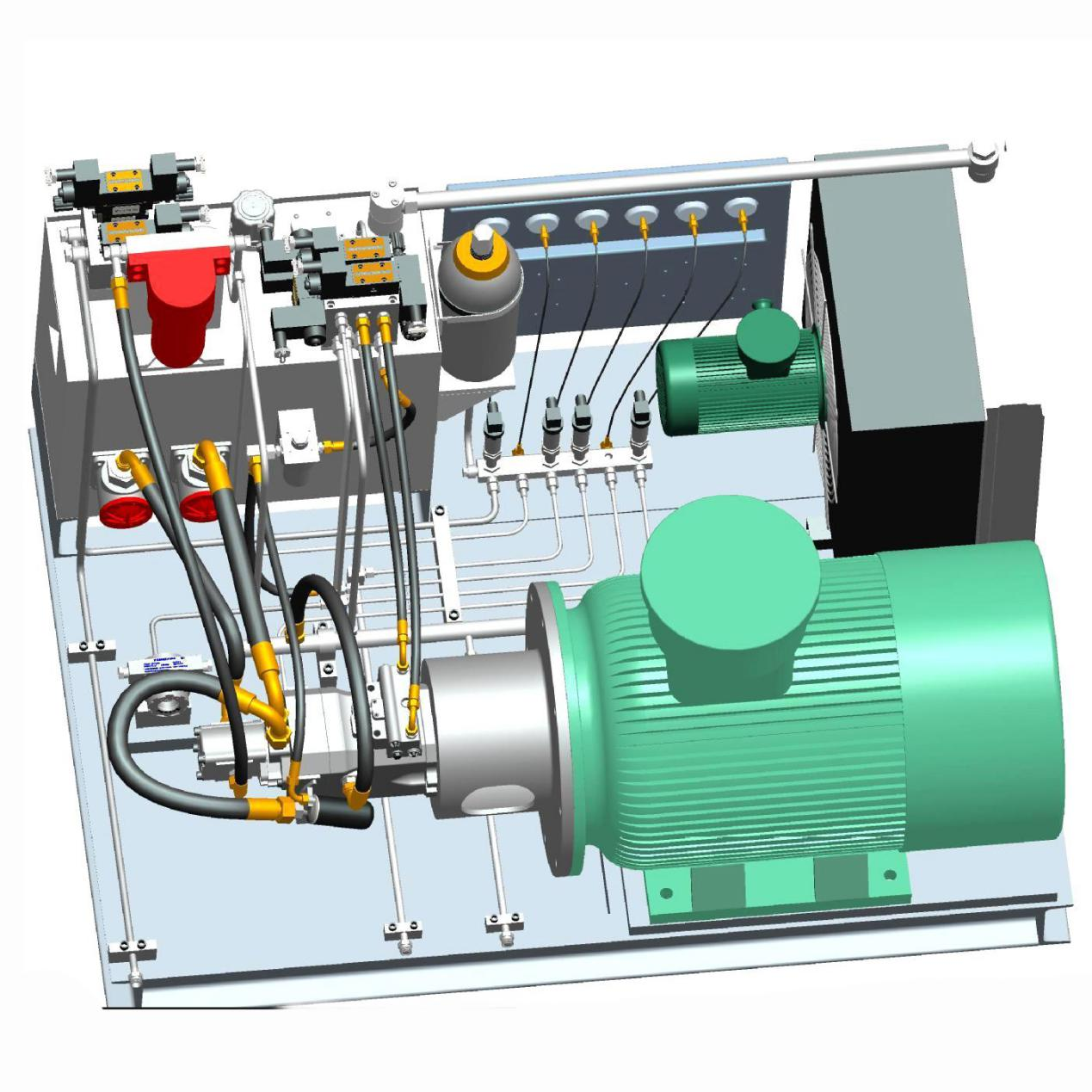
Key Functions of a Hydraulic Reservoir
1. Fluid Storage: The primary role is to hold hydraulic fluid, ensuring that there is always enough fluid to meet the system's needs, including compensating for thermal expansion and contraction.
2. Cooling the Fluid: Hydraulic systems can generate significant heat during operation. The reservoir helps cool the hydraulic fluid by allowing it to rest and dissipate heat. In some cases, the reservoir is equipped with additional cooling systems like heat exchangers or fans.
3. Contaminant Settling and Filtering: The hydraulic reservoir allows solid particles and contaminants to settle at the bottom, keeping them from circulating through the system. This reduces wear on components. Filters may also be incorporated in the reservoir to improve fluid cleanliness.
4. Air De-Aeration: Hydraulic fluid can become aerated during operation, which affects system performance. The reservoir provides a space for air bubbles to escape from the fluid before it reenters the system, ensuring consistent performance.
5. Fluid Conditioning: Reservoirs allow hydraulic fluid to reach the desired temperature and condition before being circulated. Fluid entering the reservoir is often at a high temperature or pressure, and the tank helps normalize this before the fluid is pumped back into the system.
6. Compensation for Fluid Expansion/Contraction: As the fluid heats up, it expands, and when it cools down, it contracts. The reservoir compensates for these volume changes, ensuring that the system remains properly pressurized and functional.
Importance of a Hydraulic Reservoir in the Hydraulic System
The hydraulic reservoir is essential for the proper operation, efficiency, and longevity of the hydraulic system. Its importance can be seen through several key aspects:
1. Fluid Supply:
- Without a sufficient supply of fluid, the hydraulic system cannot function. The reservoir stores the fluid and ensures that the system has enough fluid even when accounting for fluid loss, leakage, or thermal expansion.
2. Heat Dissipation:
- Hydraulic systems can generate heat, which, if not properly managed, can reduce system efficiency and damage components. The reservoir helps by cooling the fluid as it rests, preventing overheating. This also extends the life of seals, pumps, valves, and other components.
3. System Efficiency:
- A properly designed reservoir helps maintain consistent fluid temperature, pressure, and cleanliness, all of which contribute to more efficient system operation. Fluid that is too hot, dirty, or aerated can cause system failure or degradation in performance.
4. Fluid De-Aeration:
- Air in the hydraulic fluid can lead to cavitation, erratic system operation, and decreased efficiency. The reservoir ensures that air bubbles rise to the surface and dissipate, helping to maintain smooth system operation.
5. Contaminant Removal:
- Hydraulic fluid can carry contaminants like dirt, metal particles, and water, which can damage sensitive components. A reservoir provides space for these contaminants to settle and can incorporate filtration to further purify the fluid before it is circulated.
6. Pressure Regulation and Compensation:
- As the system operates and the fluid heats up or cools down, the reservoir compensates for changes in fluid volume and pressure. Without this, pressure imbalances could cause system malfunctions or damage components.
Design Considerations for Hydraulic Reservoirs
When designing or choosing a hydraulic reservoir, several factors must be considered:
1. Capacity: The reservoir should be large enough to store sufficient hydraulic fluid, usually 2-3 times the pump’s flow rate per minute, to allow for cooling and settling of contaminants.
2. Shape and Orientation: A horizontal tank allows for better heat dissipation and contaminant settling, whereas a vertical tank takes up less floor space.
3. Material: Common materials include steel, aluminum, or plastic. The choice depends on the system's pressure, temperature, and environmental conditions.
4. Ventilation and Breathers: These prevent the buildup of pressure and allow the system to breathe as fluid levels change.
5. Filtration: Filters are often integrated into reservoirs to remove contaminants from the fluid as it circulates through the system.
6. Heat Exchangers: In high-heat applications, heat exchangers or cooling fans can be added to the reservoir to enhance heat dissipation.
Conclusion
The hydraulic reservoir is a vital component in a hydraulic system, acting as a fluid storage tank, heat exchanger, air separator, and contaminant trap. It ensures the system has the correct amount of fluid, maintains fluid quality, and manages temperature and pressure fluctuations. Proper sizing, design, and maintenance of the hydraulic reservoir are critical for the efficient, reliable, and long-term operation of the entire hydraulic system.
HCIC is a professional hydraulic manufacturer, mainly engaged in hydraulic system design, manufacture, installation, transformation, commissioning and hydraulic components brand sales and technical services.We hope that our product can help to save your cost and improve your quality. For More details please email us "[email protected]" or google search "HCIC hydraulic"

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 CA
CA
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 KA
KA













