What is the principle behind electric actuators
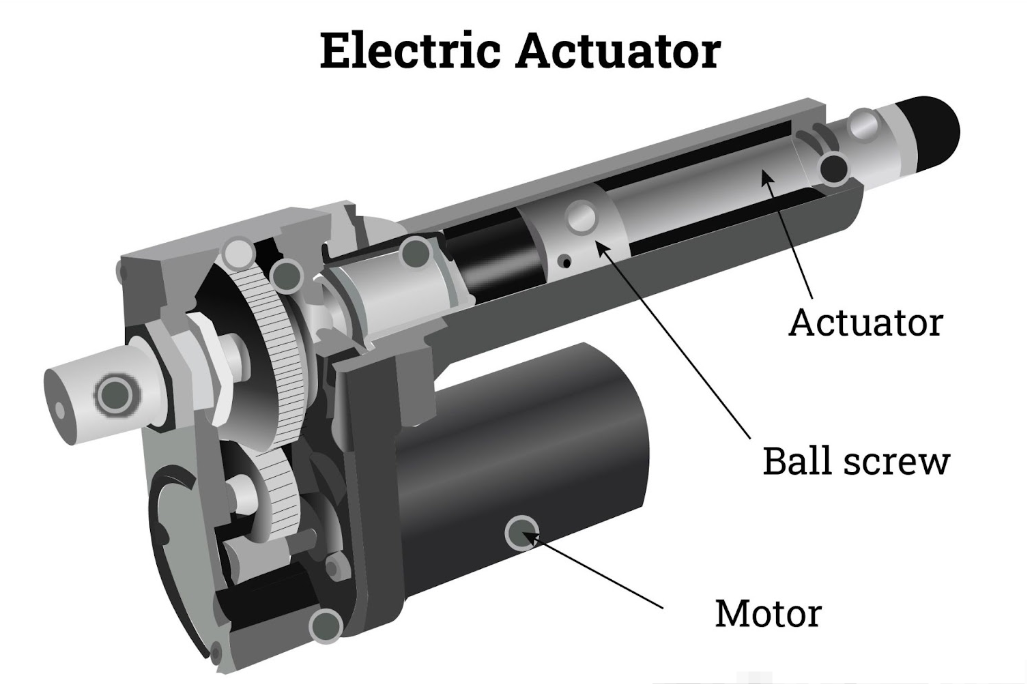
1. Electric Motor
The electric motor is the heart of the actuator. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. There are two main types of motors used in electric actuators:
- DC Motors: These motors are powered by direct current and are known for their simplicity and ease of control. They are often used in applications requiring precise speed and position control.
- AC Motors: These motors are powered by alternating current and are typically used in applications requiring high power and efficiency. They are more complex to control compared to DC motors.
2. Conversion Mechanism
The conversion mechanism transforms the rotary motion of the motor into the desired type of motion:
- Lead Screw Mechanism: In linear actuators, a lead screw (or ball screw) is used to convert the rotary motion into linear motion. The screw rotates, causing a nut to move along its length, which in turn moves the actuator's output shaft.
- Gear Mechanism: In rotary actuators, gears are often used to adjust the speed and torque of the motor's output. The motor's rotary motion is directly used to turn a shaft or other mechanism.
3. Control System
The control system manages the actuator's operation. It interprets input signals and adjusts the actuator's movement accordingly:
- Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): This technique controls the motor's speed by varying the width of the pulses in a pulse train. It is commonly used in DC motors.
- Voltage Control: By varying the voltage supplied to the motor, the speed and direction of the actuator can be controlled.
- Current Loops: In some applications, current loops are used to provide precise control over the actuator's position and speed.
4. Feedback Mechanism
Feedback mechanisms are crucial for applications requiring high precision and repeatability:
- Encoders: These devices provide feedback on the position and speed of the actuator. They can be optical, magnetic, or mechanical.
- Potentiometers: These are variable resistors that provide feedback on the position of the actuator. They are simpler and less expensive than encoders but offer lower precision.
5. Power Supply
The power supply provides the necessary electrical energy to the actuator. It can be a simple battery or a more complex power supply unit, depending on the application:
- Battery: Portable applications often use batteries to power the actuator.
- Power Supply Unit: For stationary applications, a power supply unit converts AC power from the mains into the required DC power for the actuator.
Applications of Electric Actuators
Electric actuators are used in a wide range of applications due to their versatility and precision:
- Robotics: Electric actuators are used to control the movement of robotic arms and other components.
- Automotive: They are used in various automotive systems, such as power windows, seat adjustments, and throttle control.
- Aerospace: Electric actuators are used in aircraft control systems, such as flaps and landing gear.
- Manufacturing: They are used in automated machinery and assembly lines to control the movement of parts and tools.
Electric actuators offer several advantages, including precise control, ease of integration with electronic systems, and the ability to operate in a wide range of environments. They are an essential component in modern automation and control systems.HCIC is a professional hydraulic manufacturer, mainly engaged in hydraulic system design, manufacture, installation, transformation, commissioning and hydraulic components brand sales and technical services.We hope that our product can help to save your cost and improve your quality. For More details please email us "[email protected]" or google search "HCIC hydraulic"

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 CA
CA
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 KA
KA













